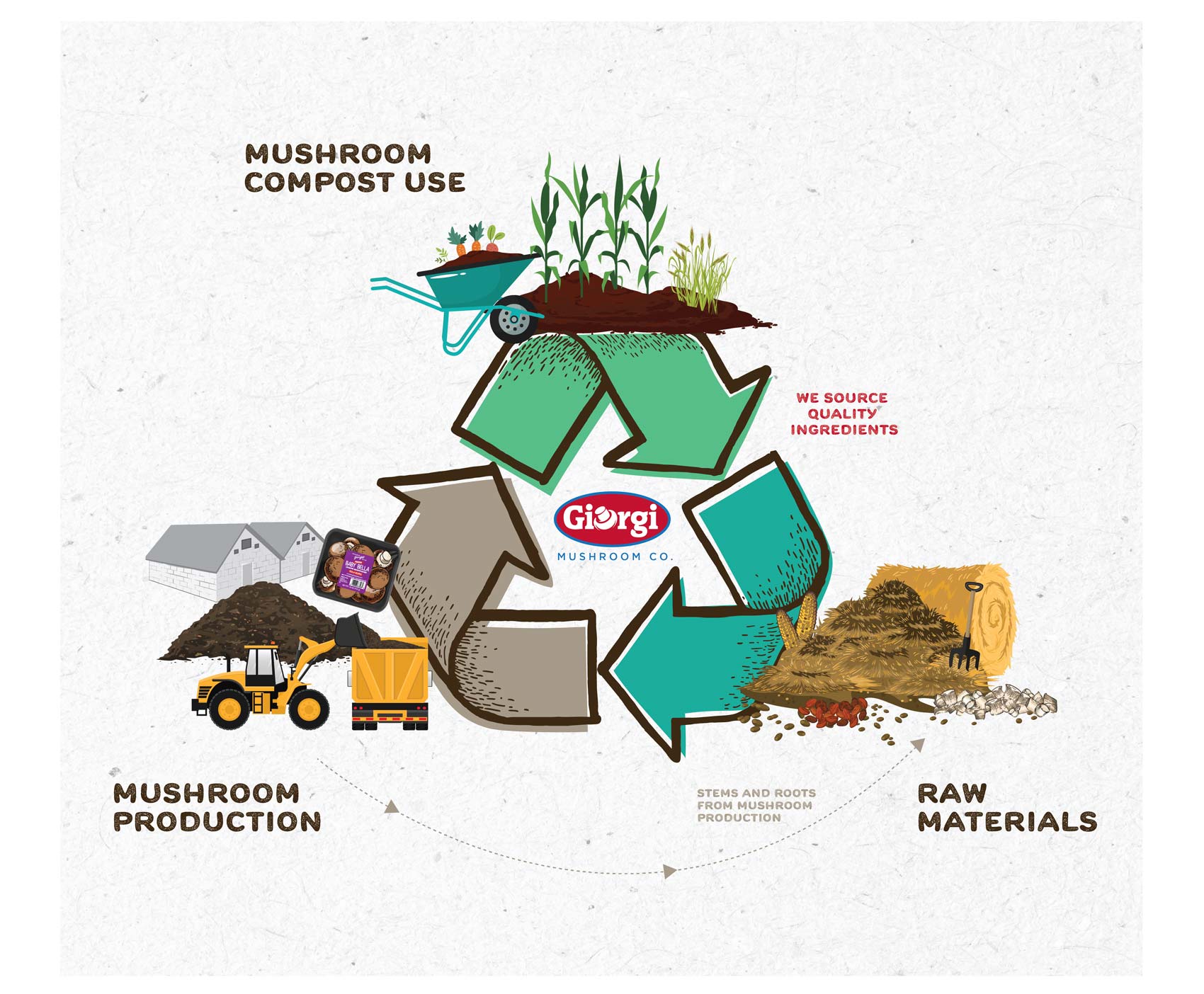
Mushroom Compost in Landscaping
Mushroom compost is a beneficial addition to both new and established lawns, flowers, shrubs, sod, and the prevention of artillery fungus.
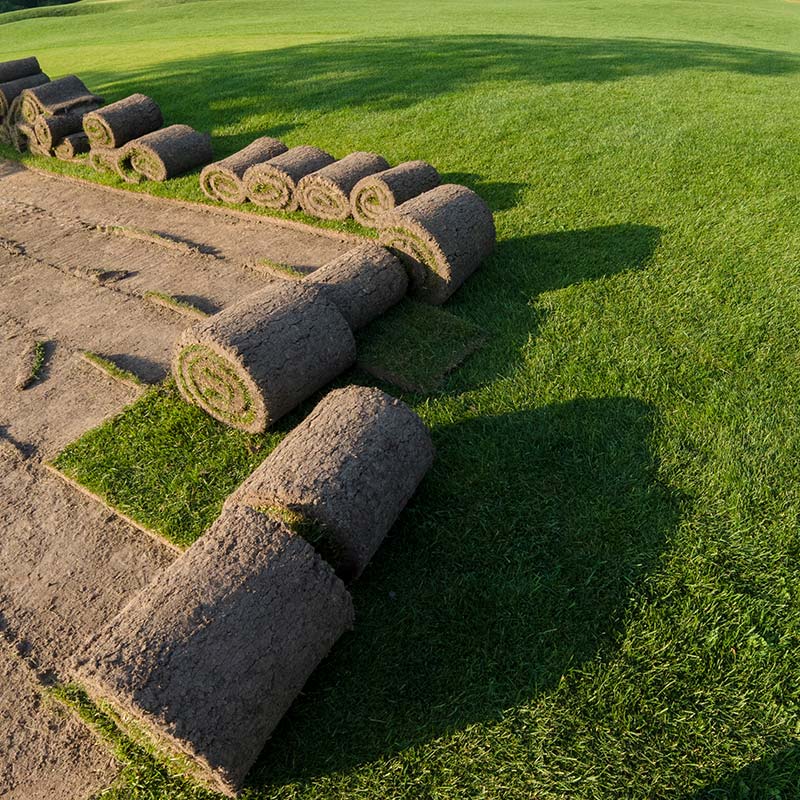
When the soil is workable (not frozen or overly wet), prepare a new lawn seed bed in the fall by applying 1-2” (3-6 yd³ per 1000’) MC and incorporate to 4-6”. Then apply seed at the recommended seeding rate and cover with ¼-½” (1-2 yd3 per 1000’) of MC. Rake the area and water well.
When overseeding an established lawn, aerate and spread ½” layer of MC over the lawns surface. Spread seed, use a flexible rake to work the seed and MC in, and water until seed germinates.
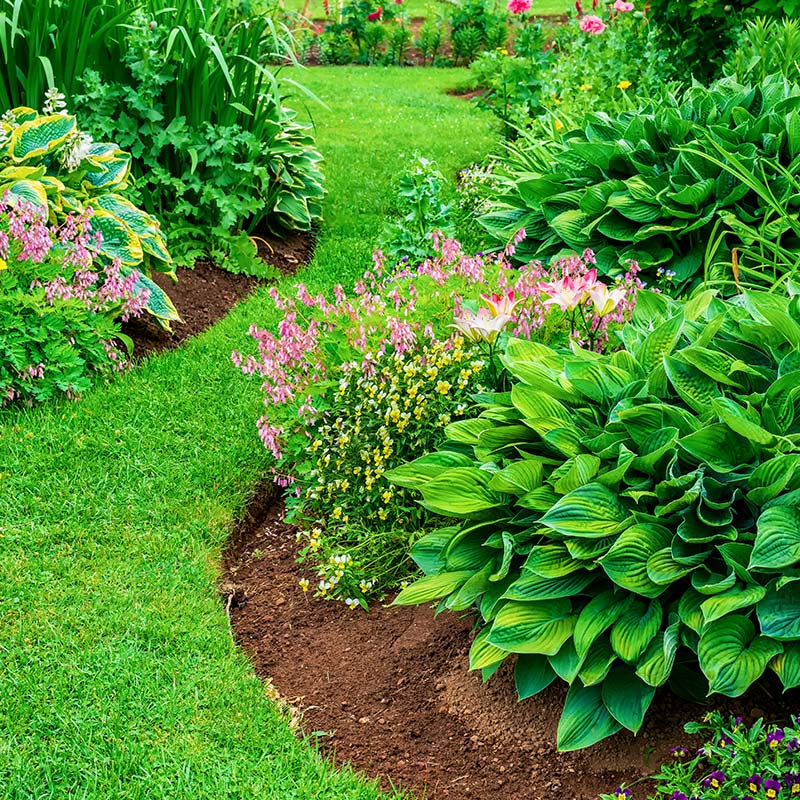
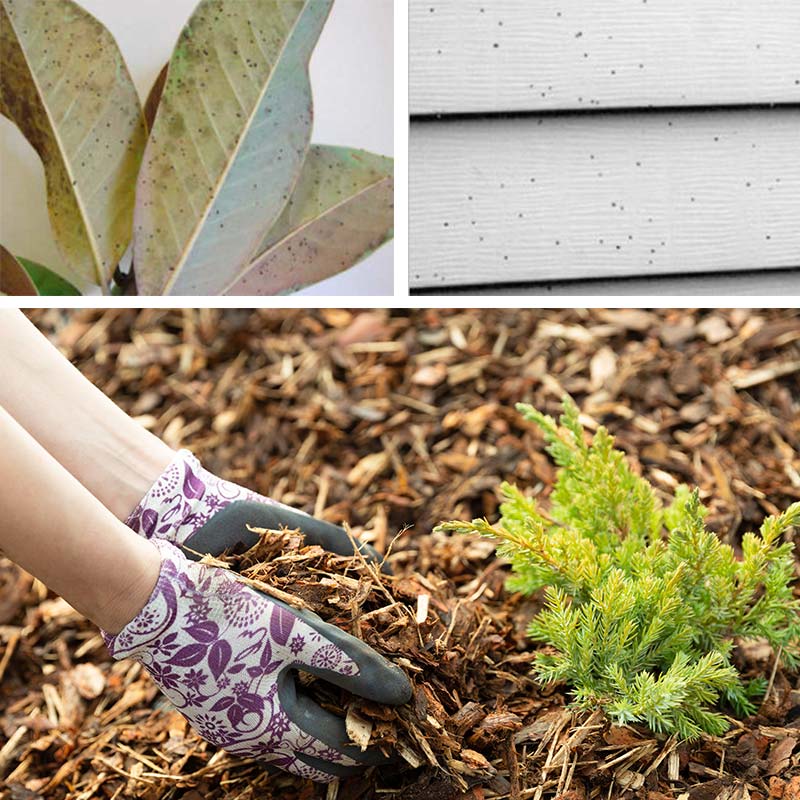
Follow new lawn recommendations to amend soils for flower and shrub beds and prior to applying sod. No other fertilizer will be needed during the first year for flowers and shrubs. Sod will root best when ½” mushroom compost is applied at the seams. Mix MC with wood-based mulches to inhibit the growth of artillery fungi (Sphaerobous sp.), which leaves permanent small black sticky spots on siding, décor, cars, and plants near mulch. As little as 20-40% MC in the mix is effective.
-

-
Beneficial for Lawns & Sod
-

-
Great for Flowers & Shrubs
-

-
Inhibits growth of Artillery Fungus
Hay Field Uses
A ½-1” (68-129 yd³ per acre) layer of MC can improve the quality and quantity of hay for 3-5 years and protect crops in times of drought. There is a 24% residual value the second year, but annual soil testing should educate fertility management and MC applications. The thin layer can be applied between each summer cutting and in the winter when the ground is frozen, but not snow-covered. In the spring, the soil is usually too wet to bring heavy equipment onto the field. Once the soil warms up, the grass quickly becomes too tall for application. Apply MC with a manure spreader, then drag the field with a drag chain, or similar equipment, perpendicular to the direct of which the MC was spread.

Generic Crop Applications
Based on the application of fresh Mushroom Compost with a mean bulk density of 574.73 lbs/yd³
1” depth (65 to 130 yd³/acre)
| Nitrogen (N) |
1.12% |
6.4 lbs/yd³ |
832 lbs/acre |
| Phosphate (P2OS) |
0.67% |
3.8 lbs/yd³ |
494 lbs/acre |
| Potash (K2O) |
1.24% |
7.1 lbs/yd³ |
923 lbs/acre |
| Organic Matter |
25.53% |
146.7 lbs/yd³ |
19,071 lbs/acre |
2” depth (260 yd³/acre)
| Nitrogen (N) |
1.12% |
6.4 lbs/yd³ |
1,664 lbs/acre |
| Phosphate (P2OS) |
0.67% |
3.8 lbs/yd³ |
988 lbs/acre |
| Potash (K2O) |
1.24% |
7.1 lbs/yd³ |
1,846 lbs/acre |
| Organic Matter |
25.53% |
146.7 lbs/yd³ |
38,142 lbs/acre |
3” depth (260 yd³/acre)
| Nitrogen (N) |
1.12% |
6.4 lbs/yd³ |
2,496 lbs/acre |
| Phosphate (P2OS) |
0.67% |
3.8 lbs/yd³ |
1,482 lbs/acre |
| Potash (K2O) |
1.24% |
7.1 lbs/yd³ |
2,769 lbs/acre |
| Organic Matter |
25.53% |
146.7 lbs/yd³ |
57,213 lbs/acre |